Inheritance Heirarchies
Introduction: 9.5.0
- If you have multiple subclasses that inherit from a superclass, they form an
inheritance heirarchy - every subclass is-a kind of a superclass
java.lang.Objectis at the top of every heirarchy, because every class inherits from object at some point
- An inheritance heirarchy is useful because it lets you inherit instance variables and methods without copying code
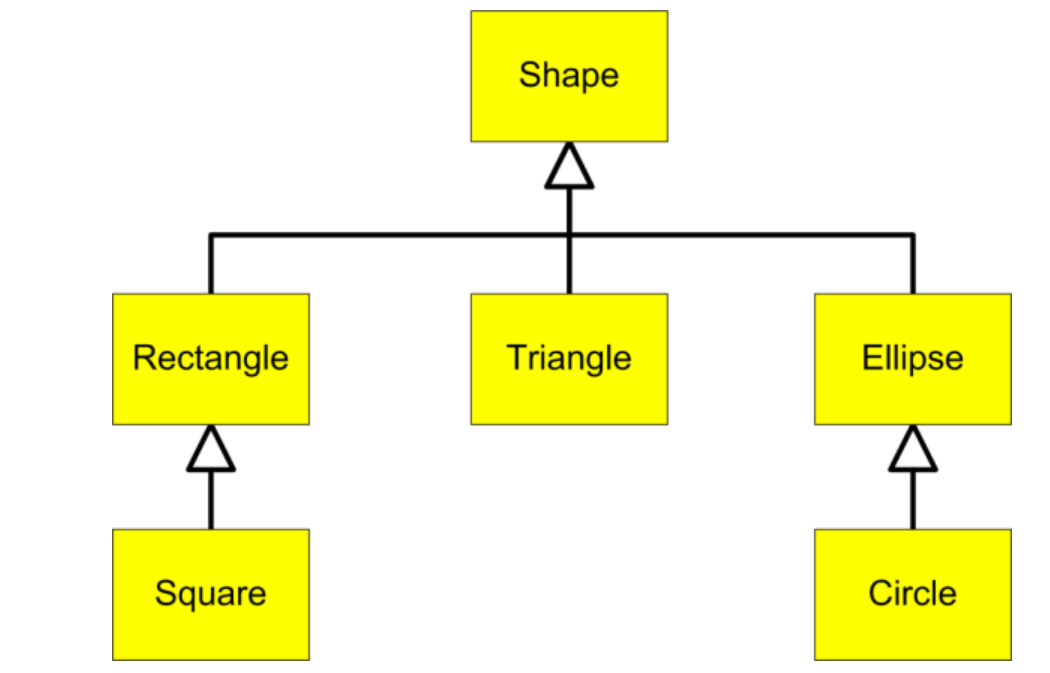
An inheritance heirarchy; this time for shapes!
Superclass References: 9.5.1
- A superclass reference variable can hold an object of that superclass or of any of its subclasses
- A Shape reference can hold a Rectangle or a Square
- Polymorphism!
- You cannot set a subclass variable to hold a superclass object
- Not all rectangles are squares!
Shape s = new Shape();
Shape shape = new Rectangle(); // valid if Rectangle extends Shape
Shape shp = new Square(); // if Square extends Rectangle and Rectangle extends Shape, you can do this :)
Square sqr = new Rectangle(); // Absolutely not!
Superclass Method Parameters: 9.5.2
- Another advantage of inheritance heirarchy is we can write methods which accept superclass types and pass in a subclass object
- Makes methods more versatile
public void geometry(Shape s) // method stub
Square sqr = new Square();
Rectangle rec = new Rectangle();
Shape shp = new Shape();
print(sqr); //valid!
print(rec); //valid!
print(shp); // valid!
Superclass Arrays and ArrayLists: 9.5.3
- Using inheritance heirarchies, we can create arrays and ArrayLists using a superclass type and put in a subclass value!
Shape[] shapeArray = { new Rectangle(), new Square(), new Shape() };
Summary: 9.5.5
- An inheritance heirarchy of subclasses inheriting from superclasses can be created to visualize an inheritance chain
java.lang.Objectis at the top of the heirarchy- When class A “is-a” class T, T is a
superclassand A is asubclass- A can be used as a reference of type T or type A
- This is called polymorphism
- Declaring references of a superclass type can be useful because it allows you to use the superclass or any subclass in that reference
- This also works for Arrays and ArrayLists
- A can be used as a reference of type T or type A

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This was adapted from the CS Awesome curriculum, which was created by
Barbara Ericson, Beryl Hoffman, and many other CS Awesome contributors. All rights reserved.
CS Awesome is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.