Scope and Access
Introduction: 5.8.0
- variable
scopeis defined as where the variable is accessible from- Determined by where you declare your variable from
- look at the nearest curly brackets!
- A variable doesn’t exist outside of it’s scope!
- Determined by where you declare your variable from
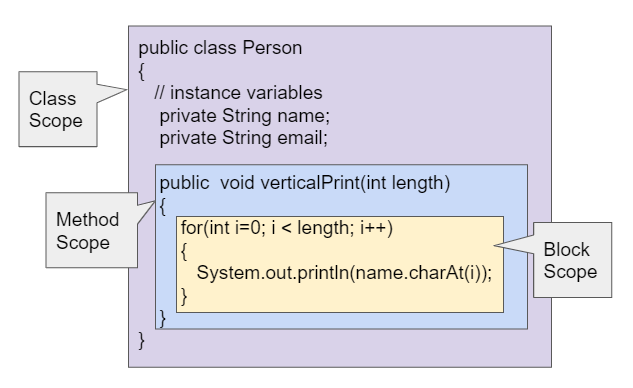
Class level scopefor instance variablesMethod level scopeforlocal variables- this includes parameter variables
block level scope- for
loop variablesand variables defined inside of blocks of code
- for
Local Variables
Local variablesare declared inside a method- These variables can only be used within the method
- they do not exist outside!
- Parameter variables are also local variables
- Use local variables for anything used in just one method
Instance variables
Instance variablesare declared at class scope- these are shared with all methods
- can be public or private
- determine accessibility outside of the class
- can be public or private
- They have class scope regardless of being public or private
Scope problems
- If a local variable has the same name as an instance variable, the local variable takes prescidense
- you can use
thisto refer to the instance variable!
- you can use
Summary: 5.8.2
Scopeis where a variable is accessible/can be usedLocal variablescan only be declared in the body of methods & constructors- cannot use modifiers like public or private
- When a local variable has the same name as an instance variable, the name will refer to the local variable
- formal parameters and variables declared in a method/constructor can only be used in that method/constructor

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This was adapted from the CS Awesome curriculum, which was created by
Barbara Ericson, Beryl Hoffman, and many other CS Awesome contributors. All rights reserved.
CS Awesome is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.